Application of Inverter in Motor Control
Using inverters to control the speed of electric motors by adjusting the frequency and voltage.
Inverter is a device that controls the motor speed by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor.
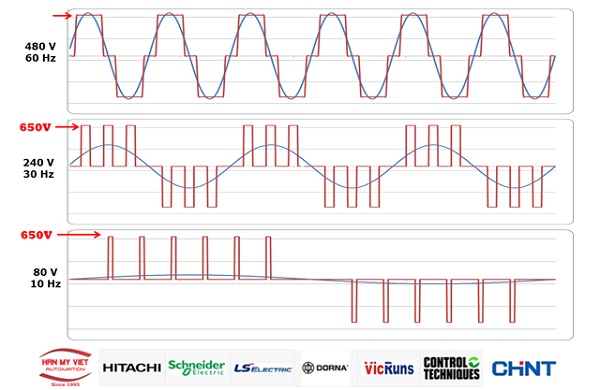
The motor's operating speed is determined by the frequency provided by the inverter; a higher frequency results in a faster motor speed.
The inverter not only has the capability to increase the speed to meet the motor's load requirements but can also flexibly reduce the speed to meet changing speed demands during operation, resulting in high efficiency and energy savings.

How Does an Inverter Work?
First, the AC power goes through a diode rectifier that converts AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current).

After being converted to DC, the current passes through a smoothing capacitor, which removes the negative phase and provides a stable DC voltage.

Finally, this DC voltage is converted back to a symmetrical three-phase AC voltage through a bipolar transistor with an isolated gate using pulse width modulation.
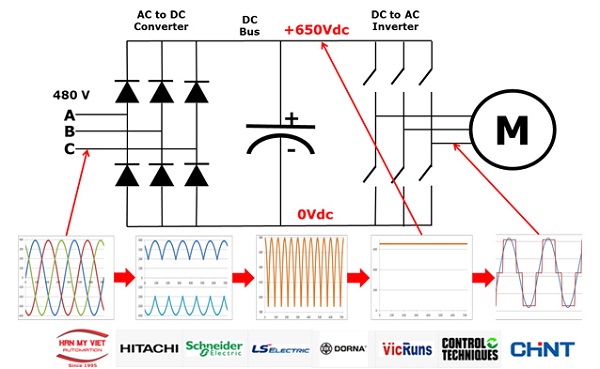
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) method is a modulation technique that varies the width of the square wave pulses, leading to changes in the output voltage.
Using PWM in inverters helps control the motor speed or maintain the motor's speed stability.
Common Faults When Using Inverter
When using an inverter, users may encounter some of the following common faults:
Overcurrent Fault: Occurs when the motor consumes more current than allowed, typically due to overload or short circuit.
Overvoltage and Undervoltage Fault: The inverter may signal a fault when the input voltage supply is too high or too low compared to the rated voltage level.
Overheat Fault: The inverter may stop operation when the internal temperature is too high, often due to an excessively hot working environment or inefficient cooling system.
Over-frequency or Under-frequency Fault: When the output frequency of the inverter is unstable or exceeds safe limits, a fault may arise.
Encoder Feedback Fault: If there is an issue with the encoder or the feedback signal from the encoder is not received, the inverter may signal a fault.
Phase Loss Fault: If one or more phases of the motor are lost, the inverter will stop operating to protect the motor.
Communication Control Fault: When there are issues in communication between the inverter and other control systems such as PLCs or computers, this fault may occur.
Understanding and early detection of these faults will help users take timely corrective actions, maintain the operating efficiency of the inverter and protect the motor from unnecessary damage.
Schneider Inverter and Common Faults
FAULT CODE | DESCRIPTION |
CbF | Circuit Break Fault |
CFF | Incorrect Configuration |
LFF3 | 4-20mA AI3 Loss |
LFFI | AI Input Signal Loss |
OCF | Overcurrent |
OLC | Process Overload |
OLF | Motor Overload |
OPF1 | One Phase Output Loss |
OPF2 | Three Phases Output Loss |
PHF | Input Phase Loss |
SCF1 | Motor Short Circuit |
SCF3 | Ground Short Circuit |
SCF4 | IGBT Short Circuit |
SLF1 | Communication Fault |
SOF | Overspeed |
USF | Undervoltage |
Hitachi Inverter and Common Faults
FAULT CODE | DESCRIPTION |
E01 | Overcurrent at Constant Speed |
E02 | Overcurrent during Deceleration |
E03 | Overcurrent during Acceleration |
E04 | Overcurrent under Other Conditions |
E05 | Overload Fault |
E06 | Brake Resistor Overload |
E07 | Overvoltage Fault |
E08 | EEPROM Fault |
E09 | Undervoltage Fault |
E10 | CT(Current transformer) Fault |
E11 | CPU Fault |
E13 | USP Fault |
E14 | Ground Fault |
E15 | Input Overvoltage |
E16 | Instantaneous Power Loss |
E20 | Overheat due to Slow Fan Speed |
E21 | Overheat Fault |
E23 | Communication Gate Array Fault |
E24 | Input Phase Loss |
E25 | Main Circuit Board Fault |
E30 | IGBT Fault |
E35 | Thermistor Fault |
E36 | Braking Fault |
E37 | Emergency Stop Fault |
E38 | Low-Speed Overload Fault |
E41 | ModBus Communication Fault |
LS Inverter and Common Faults
FAULT CODE | DESCRIPTION |
LVT | Low Voltage Fault |
OLT | Overload Trip Fault |
POT | Output Phase Loss Fault |
GFT | Ground Fault |
IOL | Inverter Overload Fault |
OCE, OC2 | Overcurrent Fault |
ERR | Communication Fault |
Applications of Inverter
Inverters are widely used in production in order to save costs by leveraging their advantages, such as reducing maintenance costs, increasing the lifespan of production equipment, and thereby enhancing production profitability.
Motor Control
Inverters have function to control the acceleration/deceleration time of motors, or protect against overload, overvoltage, undervoltage, overheating, overcurrent, and undercurrent, which helps extend the motor's lifespan and ensure smooth operation.
Additionally, inverters are commonly applied in various fields such as elevator, rolling mill, injection molding machine, winding/unwinding machine, HVAC motor system, mixer, and centrifuge…

Contact us for more information
- HAN MY VIET Ho Chi Minh City
Address: 203 - 205 Nguyen Thai Binh St., Nguyen Thai Binh Ward, Dist.1, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
Phone: (+8428) 3821 6710 – +8491 621 6710
Mail: hmv@hanmyviet.com
+ HAN MY VIET Ha Noi Branch
Address: 72 Bui Ngoc Duong St., Bach Mai Ward, Hai Ba Trung Dist., Ha Noi, Vietnam.
Phone: Ms. Hien 098.699.1948
+ HAN MY VIET Bac Ninh Branch
Address: 6 Ngoc Han Cong Chua St., Hoa Dinh Quarter, Vo Cuong Ward, Bac Ninh, Vietnam.
Phone: Mr. Tien 097.546.0366
+ HAN MY VIET Da Nang Branch
Address: 26 Tang Bat Ho St., Hai Chau II Ward, Hai Chau Dist., Da Nang, Vietnam.
Phone: Ms. Hoa 033.636.3965